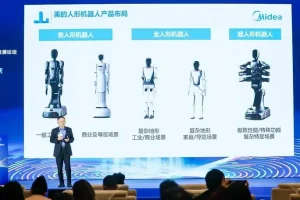
The Multi Dimensional Robot Sports Revolution
The Humanoid sports world has witnessed a remarkable step forward in 2025 with humanoid athletes emerging as much more than just a vision. While competitive events serve as ideal robotic training grounds for advancing algorithms and hardware technologies. These sophisticated machines are also revolutionizing how athletes train, recover from injuries, and how equipment manufacturers test their latest products. With the humanoid robot market projected to grow from $1.9 billion in 2025 to $11 billion by 2030. The integration of robotics into sports represents one of the most compelling opportunities for technological advancement in the athletic realm.
From intelligent sparring partners that never tire to precise rehabilitation assistants that track recovery metrics in real time. Humanoid robots are transforming every aspect of sports beyond the playing field. This comprehensive exploration examines how these advanced machines are reshaping training methodologies, injury rehabilitation, equipment testing, and venue management across the global sports industry.
Intelligent Training Partners: The Evolution of Practice
Repeatable Performance Standards
One of the most valuable applications of humanoid robots in sports training lies in their ability to deliver consistent, repeatable performance. Allowing robots to mimic athletic movements, enabling athletes to practice against a standard benchmark repeatedly.
Athletes can program robots to execute their previous best performances, creating a tangible target to surpass. Imagine a boxer training against a robot that precisely mimics their championship winning opponent’s fighting style, or a tennis player facing returns calibrated to match their fastest recorded serves. This repeatability eliminates the variability inherent in human training partners, who inevitably experience fatigue, inconsistency, or off days.
Adaptive Intelligence and Real Time Feedback
Modern humanoid training robots leverage artificial intelligence to provide sophisticated feedback mechanisms. The Pepper robot was transformed into a personal trainer capable of counting repetitions, correcting exercise errors, and storing and showing previous performances. These capabilities extend beyond simple tracking to include biomechanical analysis, form correction, and personalized training adjustments.
RoboGym’s system uses sensors to capture athlete movement in real time, identifying whether the athlete is working out in the most efficient and ergonomic motion range, with direct biofeedback helping avoid joint injuries. This level of precision monitoring was previously available only in elite training facilities with extensive human expertise and expensive equipment.
Rehabilitation Revolution: Precision Recovery
Robotic Exoskeletons and Assistive Devices
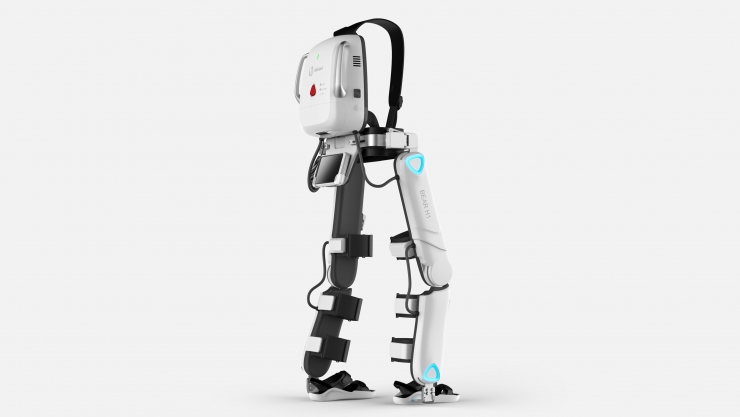
The intersection of humanoid robotics and rehabilitation represents one of the most impactful applications of this technology. Robotic exoskeletons are among the most used motor rehabilitation robots today. Connecting human like mechanical structure design with patients to form integrated, wearable mobile devices that achieve dual purposes of sports rehabilitation and physical function recovery.
These systems address the significant challenges facing rehabilitation services globally, where sports rehabilitation robots help patients with degenerative diseases recover physical abilities, reduce the burden on rehabilitation instructors, and complete quantitative assessments in a controlled and repeatable manner.
Socially Interactive Rehabilitation
The psychological dimension of rehabilitation is equally important as the physical aspects. Socially interactive humanoid robots augment rehabilitative therapies beyond standard computer interfaces, with stroke survivors who underwent long term rehabilitation preferring robot assisted therapy.
Dance therapy with a robotic partner yielded improvements in gait, balance, and disease symptoms after 3 weeks of adapted tango classes. The humanoid NAO robot has been extensively deployed for exercise games with patients, including imitation games for children and memory games for stroke rehabilitation.
Personalized Recovery Pathways
A neural learning approach for humanoid exercise robots automatically analyzes and corrects physical exercises, with the ability to train many different human partners over time requiring lifelong learning capability. The system stores information on pose and movement per frame, allowing feedback not only on pose but also on velocity of motion.
China based Fourier’s GR-2 humanoid robot, shown weight training, could assist patients performing strength training exercises for physical rehab, particularly strong for Fourier’s focus on rehabilitation technology.
Predictability and Trust in Rehabilitation
Research reveals that subjects preferred trajectory guidance interaction, recognizing it as helpful and predictable, with effort lower than with unpredictable human partners. This predictability proves crucial in rehabilitation contexts where patients need consistent, reliable support to rebuild confidence and motor function.
Safety and Spotting: Protecting Athletes
Weightlifting and Strength Training Applications
The gym environment presents numerous opportunities for humanoid robot applications in safety and spotting. Robot trainers can catch errors in real time, with yoga related injuries costing the U.S. $1.3 billion annually due to improper form. A robotic spotter could save millions while preventing injuries.
RoboGym offers professional neuromuscular training with precise control over high intensity stimulation of specific muscles, with adaptive load based on current strength fulfilling requirements of an aging society and helping avoid injuries.
Medical Emergency Response
During training sessions, humanoid robots equipped with medical monitoring capabilities can detect physiological distress signals before they become critical. Their ability to maintain constant vigilance surpasses human spotters who may momentarily divert attention. In emergency situations, robots can immediately alert medical personnel while providing precise location data within large training facilities.
Form Correction and Injury Prevention
Robots excel at precision, with AI coaches blending algorithms for form correction while virtual classes allow trainers to provide motivational support. The combination of consistent biomechanical monitoring and immediate corrective feedback significantly reduces the risk of training injuries caused by poor technique.

Crowd Management and Stewarding Excellence
Stadium Security and Surveillance
Sports venues have embraced robotics for security and crowd management with impressive results. The Sacramento Kings’ Golden 1 Center uses Knightscope robots for security, with Autonomous Data Machines including LIDAR devices, high definition low light video cameras, thermal imaging, automatic license plate recognition, and directional microphones.
Autonomous security robots function as diligent sentinels, autonomously patrolling assigned areas and actively monitoring crowds in real time, with advanced sensors identifying unusual activities or potential security threats.
Real Time Crowd Flow Management
On busy matchdays or during large scale events, autonomous robots monitor key areas, support crowd flow management, and flag unusual activity, assisting in queue management and scanning for unattended bags. These machines can perform routine patrols, surveillance sweeps, and site checks overnight, enhancing protection when human resources are scaled back.
Information and Wayfinding Services
Robots stationed as Information Kiosks serve as super human helpers, providing directions and answering questions while also supporting emergency situations related to security, health and safety with sophisticated sensors detecting unusual temperature changes, fire, and questionable CO levels.
The strategic advantage lies in mobility: unlike traditional kiosk structures, robots easily relocate to serve changing needs and traffic flow during specific events, adapting to the unique demands of different sporting occasions.
Enhanced Emergency Response
Robots equipped with audio anomaly detection capabilities sense explosions or gunshots instantly, alerting emergency personnel for rapid and educated response. In medical emergencies, people can quickly alert nearby robots to summon paramedics, while robots can help diffuse situations by calling security staff when fights or disturbances occur.
Product Testing and Development
Durability and Performance Validation
Humanoid robots serve as invaluable testing platforms for sports equipment manufacturers. Sports events serve as testing grounds for evaluating equipment durability, safety concerns, and efficiency, accelerating advancements in artificial intelligence, mechanical design, and sensor engineering.
The rigorous demands placed on robots during athletic competitions expose equipment to extreme stress conditions. YouTuber testing of an $80,000 Unitree G1 humanoid through durability tests including intense tasks ultimately destroying the robot demonstrated equipment testing capabilities. While this example was destructive, it illustrates how robots can test product limits without human injury risk.
Repeatability in Testing Protocols
Traditional product testing with human athletes introduces variables that complicate data analysis. Human fatigue, technique variation, and psychological factors all influence results. Humanoid robots eliminate these variables, executing identical movements thousands of times to generate statistically robust data on equipment performance and longevity.
Manufacturers can program robots to perform specific movements at precise force levels, angles, and speeds, mapping equipment degradation patterns with unprecedented accuracy. This capability accelerates product development cycles while reducing warranty claims through better design validation.
Material Science Applications
The World Humanoid Robot Games showcase agile robots sprinting, jumping, balancing and recovering, with advanced materials behind these remarkable machines supporting the wider robotics industry from early prototypes to field ready systems.
Sports equipment manufacturers benefit from the same material science advances that enable humanoid robot performance. High performance polymers, advanced composites, and innovative actuator designs developed for robotics directly translate to improved athletic equipment.
Safety Standards and Compliance Testing
IEEE Humanoid Working Group developed classification taxonomy to define humanoid robots, creating quantifiable stability metrics, test methods, and safety standards tailored to actively balancing robots. These standards help equipment manufacturers ensure their products meet safety requirements when tested under realistic athletic conditions.
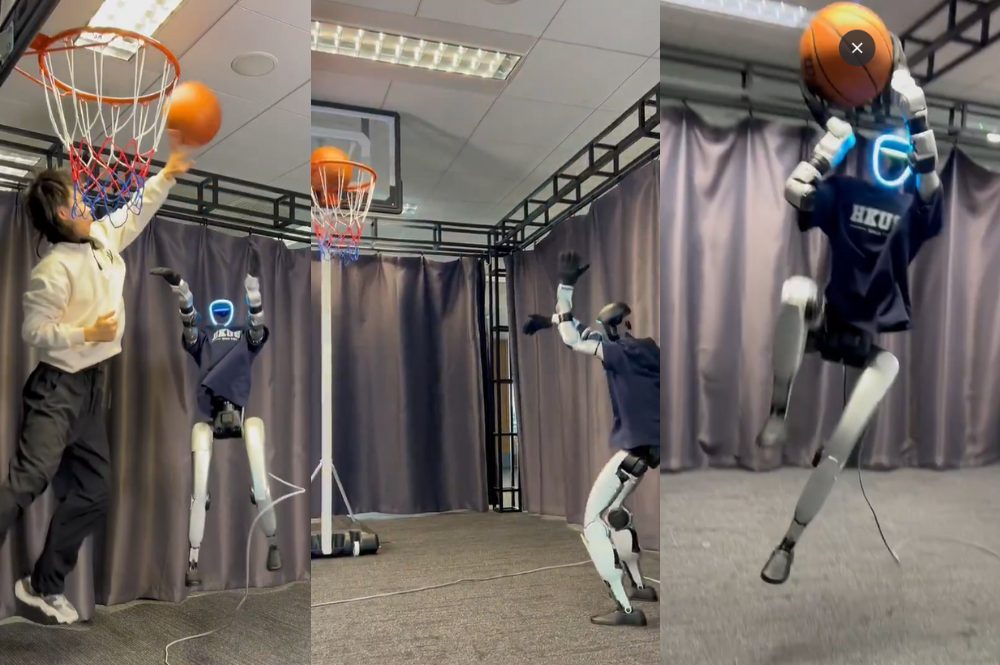
Competitive Sports: Robots as Athletes
Current State of Robot Athletics
The 2025 World Humanoid Robot Sports Games featured 11 humanoid sport events modeled after traditional human competitions including track and field, gymnastics, and soccer, designed through collaborative effort between sports professionals and robotics experts.
The robotic participants competed in 26 different sports events from running to kickboxing to soccer at the state backed tournament, with developers less focused on winning or losing and more on testing agility, endurance and battery life.
Learning from Competition
This multi dimensional event covering sports, art and application aims to anchor technology to scenarios, finding useful applications for robots on the eve of large scale mass production. Competition provides structured environments where engineers can measure progress objectively and identify improvement areas systematically.
While critics viewed previous events as publicity stunts after robots emitted smoke and failed to complete courses, industry experts recognize competitions as crucial catalysts advancing humanoid robots toward practical applications.

Future Horizons: Emerging Applications
AI Powered Coaching Systems
The next generation of humanoid training systems will integrate advanced artificial intelligence for sophisticated coaching capabilities. Artificial intelligence technology analyzes athletes’ training, tracking and analyzing characteristics of individual sports function, arrangement of training plans, brain function state, routine physiology and biochemistry indices, and nutrition regulation.
Virtual Reality Integration
Combining humanoid robots with virtual reality environments creates immersive training scenarios impossible to replicate otherwise. Athletes can practice against virtual opponents rendered through robot movements, experiencing realistic physical feedback while training for competitions in digitally simulated environments.
Personalized Training Evolution
Biometric scanning analyzes sleep patterns, stress levels, and muscle fatigue from yesterday’s workout to craft routines that adapt in real time to body needs, processing dozens of variables influencing performance including sleep quality, hydration, cortisol spikes, and lingering strains.
Data Analytics and Performance Optimization
Every interaction between athletes and humanoid robots generates valuable data. Advanced analytics transform this information into actionable insights, revealing patterns in performance, identifying injury risk factors, and optimizing training loads. The integration of this data with wearable sensors creates comprehensive athlete monitoring systems.
Economic and Practical Considerations
Cost Benefit Analysis
Knightscope robots are leased rather than owned, with cost never coming up in security discussions because it’s so much less expensive than having guards, suggesting even high schools could benefit.
Initial investment in humanoid robotics requires significant capital, but long term operational costs often prove lower than human equivalents. Robots don’t require salaries, benefits, sick leave, or vacation time. They operate consistently for extended periods, delivering predictable performance without the variability inherent in human workers.
Maintenance and Reliability
Humanoid robots present unique design challenges with dozens or hundreds of joints and moving parts that need to work in tandem, where even one failure may require the entire robot to go offline for maintenance. Future maintenance free components won’t need replacement as often and don’t require regular maintenance, leading to vastly reduced costs over the robot’s entire lifespan.
Integration Challenges
Successfully deploying humanoid robots requires careful planning around infrastructure, staff training, and system integration. Implementation of robotic systems in clinical practice faces lack of adequate infrastructure and staff training as significant implementation challenges. Sports organizations face similar hurdles when introducing robotic systems.
Safety and Regulatory Framework
Humanoid robots pose unique safety risks driving a push for new standards before they start sharing workplaces and homes, with robots sometimes falling and requiring restriction to defined areas separated from human workers by physical panels or laser barriers.
Ethical and Social Considerations
Human Robot Interaction Psychology
The acceptance of humanoid robots in sports depends significantly on human psychological responses. People instinctively recognize and respond to human like figures, with this immediate visibility establishing authority and presence critical for both deterrence and engagement.
Job Displacement Concerns
The introduction of robots inevitably raises questions about human employment. Rather than wholesale replacement, the most successful implementations position robots as tools that augment human capabilities, handling repetitive or dangerous tasks while freeing human workers for higher value activities requiring judgment, creativity, and emotional intelligence.
Privacy and Data Security
Every rep, heartbeat, and breath in a robotic gym generates data, raising ethical questions about who owns workout data, with Peloton facing lawsuits for selling anonymized user data to health insurers. Sports organizations must establish clear policies protecting athlete privacy while leveraging data for performance improvement.
Conclusion: The Integrated Future of Sports Robotics
Humanoid robots have evolved far beyond their initial conception as novelty competitors. Tomorrow, these sophisticated machines will serve as tireless training partners, precise rehabilitation assistants, vigilant safety monitors, and invaluable testing platforms. The convergence of artificial intelligence, advanced materials science, and refined mechanical engineering continues expanding the possibilities for robotic applications in sports.
The true value of humanoid robotics infrastructure in sports lies not in replacing humans but in extending human capabilities. Athletes train more effectively with consistent robotic partners. Injured athletes recover more completely with precise robotic rehabilitation support. Sports venues operate more safely with robotic security systems. Equipment manufacturers develop better products through robotic testing protocols.
As the technology matures and costs decline, humanoid robots will become increasingly common across the sports landscape. The market’s projected growth to $11 billion by 2030 reflects not just technological advancement but recognition of robots’ practical value in solving real world sports challenges.
The future of sports robotics is not about machines competing against humans for supremacy, but about machines and humans working together to push the boundaries of athletic achievement, safety, and innovation. From grassroots youth sports to elite professional competitions, humanoid robots are reshaping how we train, compete, recover, and enjoy sports, creating a more precise, safer, and more accessible athletic future for everyone.
Looking for more action? Discover which Humanoid Robot Sports could become established first