The era of humanoid robot sports has arrived. In August 2025, over 500 bipedal robots from 16 countries competed in the world’s first humanoid robot games in Beijing, showcasing capabilities in soccer, boxing, track and field, and even tai chi. As the humanoid robot market accelerates toward a projected value between $30 billion and $181 billion by 2035, the question isn’t whether robots will compete in sports, it’s which sports they’ll dominate first. Discover the future of Humanoid Sports
The Current State of Humanoid Robot Sports
Humanoid robotics has reached an inflection point. Recent competitions have demonstrated that robots can now run, fight, kick soccer balls, and perform gymnastics, albeit with varying degrees of success. China’s investment in embodied artificial intelligence has accelerated development, with the country expected to deploy over 302 million humanoid robots by 2050, compared to just 77 million projected in the United States.
The technology underlying these mechanical athletes has advanced rapidly. Modern humanoid robots feature joints generating up to 120 newton meters of torque, high precision movement control, and AI powered decision making systems that allow them to learn from past mistakes through reinforcement learning and motion capture training.
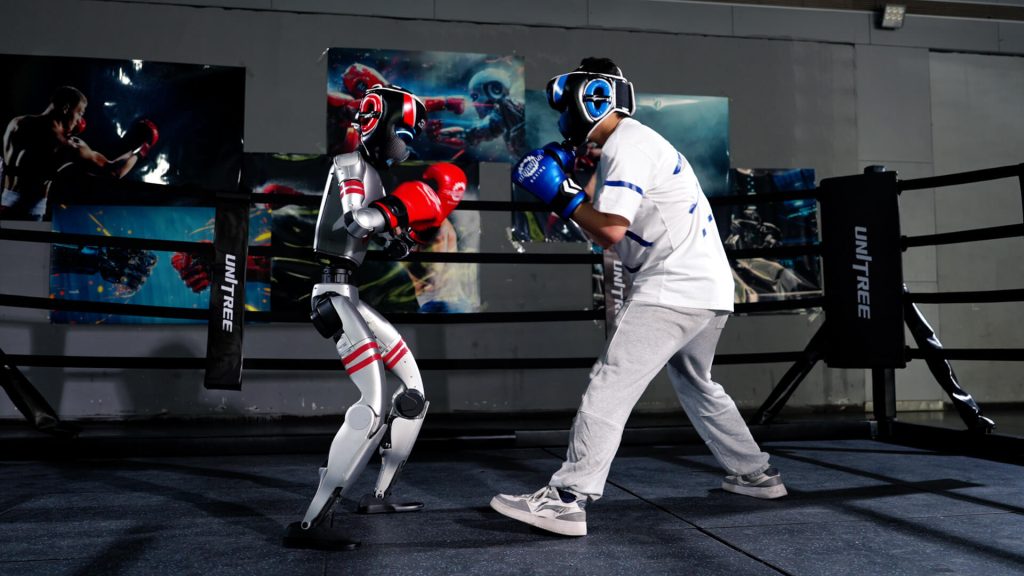

Combat Sports: The Early Frontrunner
Boxing, Kickboxing & MMA
Probability of Success: Very High
Combat sports have emerged as the most promising category for humanoid robot competition. In May 2025, China hosted the world’s first humanoid robot boxing tournament, with robots demonstrating impressive capabilities including straight punches, hook punches, sidekicks, and aerial spin kicks.
Why Combat Sports Work:
- Technical feasibility: Fighting requires full body coordination that tests robot capabilities without requiring precision object manipulation
- Entertainment value: The spectacle of robots exchanging blows draws significant viewer interest, even when movements are somewhat clumsy
- Safety advantages: Unlike human combat sports, robots can sustain damage without ethical concerns about brain injuries or long term health effects
- Existing infrastructure: Organizations like Ultimate Fighting Bots (UFB) are already organizing events in the United States and internationally
Revenue Potential: Combat robot sports offer multiple revenue streams including ticket sales, streaming rights, sponsorships, and merchandise. The entertainment factor could mirror traditional boxing or MMA economics, but with lower insurance and regulatory costs.
Gambling Integration: Robot boxing presents unique betting opportunities. Unlike human athletes whose performance can vary due to psychology or health, robot performance is more data driven and predictable, making odds calculations potentially more sophisticated. Betting markets could emerge around metrics like successful strike percentage, knockdown rates, and battery endurance.
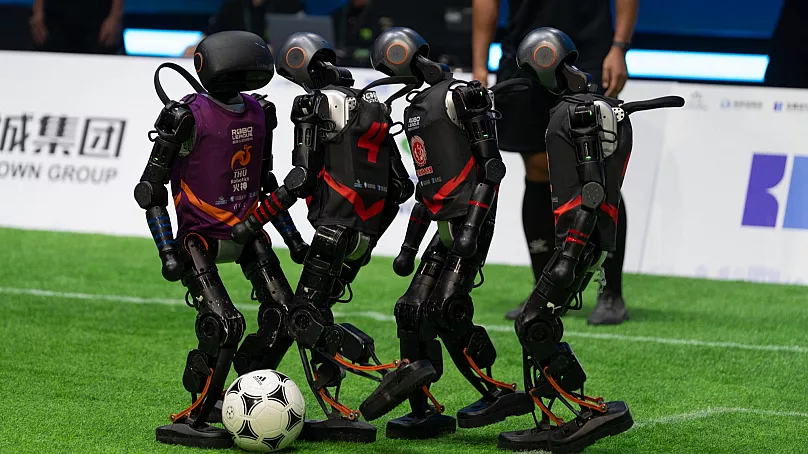
Soccer: The Long Game
Probability of Success: High (Long term)
RoboCup, founded in 1996, has an audacious goal: by the middle of the 21st century, create a team of fully autonomous humanoid robots capable of defeating the FIFA World Cup champions. While we’re far from that milestone, soccer remains a crucial testing ground for humanoid capabilities.
Recent competitions have shown robots awkwardly kicking balls and occasionally toppling over teammates, but the progress trajectory is steep. 3v3 and 5v5 matches are already being held, testing group collaboration and real time decision making.
Key Advantages:
- Established competitive framework: Decades of RoboCup development provide structure and benchmarks
- Global appeal: Soccer’s worldwide popularity ensures built in fan interest
- Technical challenge: The complexity drives innovation in perception, planning, and coordinated movement
- Sponsorship potential: Technology companies and traditional sports brands could invest heavily
Challenges:
- Ball control and passing precision remain difficult
- Group coordination algorithms need significant refinement
- The sport’s complexity means full autonomy will take longer than individual sports
Gambling Angle: Once robots achieve consistent performance, soccer betting could become sophisticated, with live odds adjusting based on real time ball possession statistics, successful pass completion rates, and positioning algorithms.
Track and Field: Speed Demons
Probability of Success: Very High
Humanoid robots have already competed in running events, with Unitree’s H1 robot winning gold in both 400m and 1,500m races at the 2025 World Humanoid Robot Games. Running represents one of the most straightforward challenges for bipedal robots.
Why It Works:
- Measurable progression: Times are objective, allowing clear improvement tracking
- Lower complexity: Straight line running is simpler than sports requiring object manipulation
- Spectator appeal: Racing has universal appeal and easy to understand formats
- Existing participation: 21 humanoid robots competed in a Beijing half marathon (though only six finished)
Future Potential: Sprint races (100m, 200m) and middle distance events (400m-1500m) will likely mature quickly. Marathon events may take longer due to battery limitations, but as energy efficiency improves, endurance racing could become a showcase for engineering excellence.
Betting Opportunities: Track and field offers straightforward betting markets, winner picks, over/under times, and head to head matchups. Performance data from training runs would make odds highly analytical.
The Revolutionary Concept: Humanoid Royale
Probability of Success: Extremely High
The most innovative and potentially lucrative format for humanoid robot sports may be something entirely new: Humanoid Royale, a battle royale competition featuring dozens of humanoid robots competing simultaneously in a shrinking arena.
Why Humanoid Royale Could Dominate
Entertainment Factor: Battle royale formats have proven wildly successful in esports, with games like PUBG Mobile drawing over 134 million viewer hours in 2023 and Fortnite achieving mainstream cultural status. The format’s inherent unpredictability, multiple simultaneous storylines, and winner takes all tension create compelling viewing.
Technological Showcase: A Humanoid Royale would test multiple capabilities simultaneously:
- Navigation and environmental awareness in a dynamic arena
- Strategic decision making and positioning
- Combat effectiveness
- Resource management (weapon/tool collection)
- Survival instinct programming
Format Possibilities:
- Arena based combat: 50-100 humanoid robots dropped into a shrinking zone, last robot standing wins
- Mixed capabilities: Robots with different strengths (speed, strength, strategy) creating diverse gameplay
- Environmental hazards: Obstacles, elevation changes, and destructible elements adding complexity
- Team modes: Squad based formats with 2-4 robots working together
Revenue Potential: This format could be transformative:
- Streaming dominance: Live broadcasts on platforms like Twitch, YouTube, and emerging metaverse spaces
- Sponsorship opportunities: Each robot could be sponsored by different companies, with branded aesthetics and capabilities
- Merchandising: Robot “characters” with unique designs could generate toy sales and collectibles
- Franchise model: Regional leagues leading to world championships, similar to esports structures
Gambling Revolution: Humanoid Royale presents the most sophisticated betting ecosystem:
- Pre match betting: Winner picks, top-3 finishes, first elimination
- Live betting: Real time odds adjusting as robots are eliminated, position changes, and strategies unfold
- Prop bets: Most eliminations, longest survival time, specific matchup outcomes
- Fantasy leagues: Participants draft robot teams and score points based on performance metrics
The data rich nature of robot competition means AI powered betting bots could analyze thousands of performance variables in real time, creating a new frontier for sports gambling technology.
Development Timeline: Early exhibitions could begin within 2-3 years, with established leagues by 2030. The format’s flexibility allows for progressive complexity as technology advances.
Gymnastics and Dance: The Aesthetic Challenge
Probability of Success: Medium High
The 2025 World Humanoid Robot Games featured artistic gymnastics and dance competitions, with judges evaluating smoothness and precision. While these robots won’t match human grace soon, progress is notable.
Advantages:
- Predetermined routines: Unlike reactive sports, routines can be programmed and perfected through repetition
- Visual spectacle: Coordinated group performances (like those at China’s Spring Festival Gala) demonstrate entertainment value
- Technical prestige: Success in precision movement showcases advanced engineering
Challenges:
- Subjective judging criteria are harder to standardize
- Less inherent competitiveness compared to direct confrontation sports
- Narrower audience appeal than combat or team sports
Market Position: These events will likely serve as exhibition showcases at larger robot sports competitions rather than standalone attractions, though culturally significant events could draw substantial audiences in Asia.
Basketball: The Height Advantage
Probability of Success: Medium
Basketball presents interesting opportunities and challenges for humanoid robots. While shooting mechanics are relatively straightforward, dribbling, passing, and defensive coordination remain complex.
Why It Could Work:
- Customizable height: Robots can be built to optimal heights for basketball, potentially making gameplay more spectacular than human basketball
- Shooting precision: With proper calibration, robot shooting accuracy could eventually exceed human capabilities
- Fast paced action: The constant movement keeps viewers engaged
Barriers:
- Dribbling while moving requires sophisticated real time object control
- Team coordination is extremely complex
- Court coverage demands substantial battery life and movement efficiency
Timeline: Simplified formats (H-O-R-S-E competitions, three point contests) will arrive before full five vs five games become viable, likely in the 2030-2035 timeframe.
Tennis and Racquet Sports: Precision Required
Probability of Success: Medium Low (Near term)
Tennis robots already exist for practice purposes, but competitive humanoid tennis faces significant hurdles. The precision required for racquet control, the speed of reactions needed, and the court coverage demand make this sport technically challenging.
Potential: As dexterous hand technology improves, a current focus for humanoid developers, racquet sports may become more feasible. However, simpler formats like table tennis or badminton (which was demonstrated at the 2025 games) will likely precede full tennis competition.


The Business Case: Why Companies Are Investing
The humanoid robot sports market isn’t just about entertainment, it’s a strategic investment in technology development and commercial applications.
Market Size and Growth
Multiple forecasts predict explosive growth:
- Goldman Sachs projects the humanoid robot market reaching $38 billion by 2035
- Some analysts forecast $181.9 billion by 2035 with a 37% CAGR
- Entertainment applications are expected to dominate early adoption through 2030
Technology Transfer
Sports competitions accelerate development in areas directly applicable to commercial robots:
- Balance and stability algorithms for factory robots
- Real time decision making for service industry applications
- Durability testing for consumer products
- Human robot interaction protocols for healthcare assistants
Brand Building
Companies like Unitree, Tesla, UBTECH, and Agility Robotics use sports competitions to demonstrate capabilities and build public recognition. A robot that wins a high profile competition becomes a marketing asset worth millions.
Safety Considerations: The Robot Advantage
One underappreciated benefit of humanoid robot sports is the elimination of athlete safety concerns that plague human sports:
- No concussions or CTE: Combat sports can be more aggressive without ethical concerns about brain injuries
- No career ending injuries: A damaged robot is a maintenance issue, not a human tragedy
- Unlimited training: Robots can practice dangerous maneuvers repeatedly without fatigue or injury risk
- Transparent enhancement: Unlike PED scandals in human sports, robot upgrades are expected and can be regulated transparently
This safety advantage may allow robot sports to explore formats and intensity levels impossible in human competition.
The Fan Experience: Building the Ecosystem
For humanoid robot sports to succeed commercially, they need engaged fan bases. Early indicators are promising:
Cultural Acceptance: China’s massive investment and public events demonstrate government and citizen buy in. The 2025 World Humanoid Robot Games drew international participation from 16 countries, showing global interest.
Personality Development: Successful sports need personalities. Organizers are already creating character profiles for competing robots, with names like “The Disruptor” and backstories that humanize the machines. This WWE style storytelling could bridge the gap between pure technology demonstration and emotional fan engagement.
Accessibility: Unlike human elite sports requiring rare genetic gifts and decades of training, robot sports could be more democratically accessible. Universities, companies, and even hobbyist teams could field competitive entries, creating grassroots participation.
Multi Platform Engagement:
- Live events: In person attendance at Olympic venues and purpose built robot arenas
- Streaming: Global audiences watching via Twitch, YouTube, and emerging metaverse platforms
- Interactive features: AR overlays showing robot sensor data, AI decision making processes, and performance statistics
- Gaming integration: Parallel esports competitions where players control virtual versions of real robot competitors
Regulatory and Ethical Framework
As humanoid robot sports grow, governance structures will emerge:
Competition Classes: Similar to weight classes in boxing, robots will likely be divided by:
- Size and weight categories
- Autonomy level (fully autonomous vs. human assisted vs. remote controlled)
- Hardware specifications and cost caps
- Software and AI capabilities
Standards Bodies: Organizations like RoboCup provide models for rule setting, but professional robot sports will need international governing bodies similar to FIFA, NBA, or Olympic committees.
Fairness Questions: How do you balance innovation with competitive fairness? Rich teams could afford better hardware, creating inequality. Solutions might include:
- Standardized chassis with customizable software
- Open source AI sharing requirements
- Cost caps on competing robots
- Regular hardware generation cycles, like Formula 1 regulations
The Future of Humanoid Sports: When Will These Sports Mature?
Based on current technological trajectories and market analysis:
2025-2027: Early adopter phase
- Continued exhibition matches and experimental competitions
- Combat sports and track and field establishing regular competition schedules
- First dedicated robot sports venues opening
- Total market value: $2-8 billion
2027-2030: Establishment phase
- First professional robot sports leagues launching
- Humanoid Royale format debuts and gains popularity
- Major sponsor commitments from technology and automotive companies
- Television and streaming deals signed
- Global viewership reaching tens of millions for major events
- Total market value: $10-30 billion
2030-2035: Mainstream acceptance
- Robot sports regularly featured alongside human sports on major networks
- World championships in multiple disciplines with substantial prize pools
- Integration with Olympic or World Games programs debated
- Advanced gambling markets fully operational
- Some robot athletes developing genuine fan followings
- Total market value: $30-100+ billion
2035+: Maturity and evolution
- Potential for human robot mixed competitions in some sports
- Fully autonomous robots competing at levels approaching or exceeding human capabilities in specific sports
- New sports invented specifically for robot capabilities
- Complete gambling ecosystems with sophisticated AI driven odds and betting markets
Conclusion: The Verdict on Humanoid Robot Sports
Which sports will humanoid robots dominate first? The evidence points to a clear hierarchy:
Near term winners (2025-2028):
- Combat sports (boxing, kickboxing, martial arts) – High entertainment value, current viability, growing infrastructure
- Track and field (sprints, middle distance) – Simple mechanics, clear success metrics, broad appeal
- Humanoid Royale – Revolutionary format combining entertainment, technology showcase, and gambling potential
Medium term contenders (2028-2033): 4. Soccer – Complex but with established development pathways and massive global appeal 5. Simplified basketball/obstacle courses – Hybrid events testing multiple capabilities 6. Artistic performances – Gymnastics and synchronized movement as spectacle events
Long term possibilities (2033+): 7. Full-complexity team sports – Basketball, American football formats 8. Precision sports – Tennis, racquet sports requiring advanced manipulation 9. Extreme sports – Parkour, skateboarding, skiing formats exploiting robot durability
The most revolutionary development may be Humanoid Royale, a battle royale format that doesn’t exist in human sports but perfectly suits robot capabilities. Combining the proven entertainment value of battle royale esports with the physical presence of humanoid robots, this format could become the flagship event that brings robot sports into the mainstream.
As technology improves, betting markets mature, and audiences embrace these mechanical athletes, humanoid robot sports will transition from novelty to genuine entertainment industry powerhouse. The robots aren’t just coming to play sports, they’re creating entirely new forms of athletic competition that may eventually rival their human counterparts in popularity and commercial success.
The future of sports isn’t just human. It’s humanoid.
The HumanoidSportsNetwork is dedicated to bringing you the latest news, developments and events from the Robots Sports industry