Chinese Robotics Giant Secures $180+ Million in Cumulative Orders, Marking Historic Milestone in Humanoid Commercialization
UBTech Robotics has achieved a watershed moment in humanoid robotics commercialization, with cumulative orders for its Walker series humanoid robots reaching 1.3 billion yuan (approximately $180 million) in 2025. The figure represents the largest confirmed order book for any humanoid robotics company globally, validating that industrial humanoids have transitioned from research prototypes to commercially viable products generating significant revenue.
The milestone comes as UBTech announced its latest major contract, a 264 million yuan ($37 million) deal to deploy Walker S2 humanoid robots at China-Vietnam border crossings for traveler guidance, personnel management, patrol duties, and logistics operations. This border deployment, combined with massive automotive manufacturing contracts including a record breaking 250 million yuan single order secured in September, demonstrates unprecedented market acceptance of humanoid labor across diverse applications.
Chief Branding Officer Michael Tam revealed that 566 million yuan worth of orders secured in November 2025 alone are scheduled for delivery within the year, underscoring the company’s ability to convert contracts into deployed robots rather than speculative pre orders. As the global humanoid robot market surges toward $15.26 billion by 2030, UBTech’s commercial traction positions the Shenzhen based company as the undisputed leader in translating humanoid technology into real world industrial applications.
Breaking Down the 1.3 Billion Yuan Order Book
Major Contracts Driving Growth
UBTech’s 1.3 billion yuan cumulative order total represents a series of landmark contracts secured throughout 2025, each demonstrating expanding application areas for humanoid robots beyond controlled factory environments.
The 250 million yuan ($35 million) order secured in September ranks as UBTech’s largest single contract to date. While the customer remains undisclosed, industry sources indicate the deal involves a major Chinese enterprise deploying Walker S2 robots for embodied intelligence applications across multiple facilities. This contract alone accounts for nearly 20% of UBTech’s total 2025 order book, reflecting confidence from large industrial customers willing to commit nine figure sums to humanoid deployment.
The 264 million yuan ($37 million) border deployment contract with Fangchenggang’s humanoid robot center in Guangxi province represents UBTech’s expansion into government operations. Deliveries beginning in December will place Walker S2 robots at China-Vietnam border crossings performing tasks ranging from traveler assistance to security patrols. The strategic significance extends beyond revenue—demonstrating government confidence in humanoid reliability for sensitive applications directly impacts public perception and regulatory frameworks governing robot deployment.
The 159 million yuan ($22 million) contract for a Humanoid Robot Data Collection and Testing Center in Zigong, Sichuan province secured in November represents UBTech’s second largest order. This facility will gather operational data from deployed humanoids, creating what Chief Branding Officer Tam described as a “positive feedback loop” where real world deployment generates training data that accelerates AI capabilities, which in turn enables expanded deployments.
Additional significant contracts include the 126 million yuan ($17.8 million) Guangxi project for embodied intelligence data collection and testing center equipment, and automotive partnerships with Miee Auto worth nearly 100 million yuan ($14 million). Collectively, these contracts demonstrate diversification across government services, data infrastructure, and manufacturing sectors.
Automotive Manufacturing: The Primary Revenue Driver
The automotive sector has emerged as UBTech’s largest commercial market, with major partnerships including BYD, Dongfeng Liuzhou Motor, Geely Auto, FAW-Volkswagen Qingdao, Audi FAW, and BAIC New Energy. These automakers deploy Walker S2 robots for quality inspection, parts handling, assembly line operations, machine tending, and logistics support across production facilities.
The automotive focus proves strategically sound. Chinese automakers operating at massive scale require thousands of workers performing repetitive tasks in structured environments, precisely the conditions where current humanoid capabilities excel. Unlike consumer applications requiring general purpose abilities, automotive deployment lets robots specialize in specific workflows with clear success metrics and immediate productivity improvements.
Foxconn, the electronics manufacturing giant, has also deployed Walker S2 robots for logistics operations, extending UBTech’s reach beyond automotive into electronics assembly and supply chain management. SF Express, China’s logistics leader, uses humanoid robots for warehouse operations, validating the technology for cargo handling and distribution center applications.
These partnerships generate more than revenue, they provide operational data that accelerates development. UBTech stated that Walker series robots deployed across automotive production lines complete different tasks while accumulating extensive real world data and frontline operational experience. This continuous scenario based practice proves essential for optimizing product performance and developing production line ready, task driven solutions.
The Walker S2: Engineering Excellence Driving Commercial Success
Autonomous Battery Swapping: The Killer Feature
The Walker S2’s commercial success stems largely from its revolutionary autonomous battery swapping system, technology that enables 24/7 continuous operation without requiring human intervention for power management. The robot independently removes its depleted battery, places it in a charging station, retrieves a fully charged unit, and installs it within approximately three minutes, maintaining operation throughout the process via backup battery.
This capability solves one of humanoid robotics’ most fundamental commercial barriers. Most humanoid robots operate 1-4 hours on single battery charges, requiring extended downtime for recharging that limits practical utility. The Walker S2’s hot swapping system enables true continuous operation across multiple shifts, fundamentally changing the economic equation for industrial deployment.
For border patrol applications, autonomous battery swapping proves essential. Robots must maintain vigilance 24/7 without gaps in coverage, yet no current battery technology provides sufficient energy density for full day operation during active patrol duty. The swapping system elegantly solves this constraint, allowing borderless operation limited only by mechanical wear rather than energy storage.
Technical Specifications and Capabilities
The Walker S2 stands 176 centimeters (5 feet 9 inches) tall and features 52 degrees of freedom throughout its articulated body. Fourth generation dexterous hands with 11 degrees of freedom each enable sub millimeter precision manipulation for assembly operations, document handling, and delicate object interaction.
Payload capacity reaches 15 kilograms (33 pounds) per arm across a workspace extending from ground level to 1.8 meters, providing human scale manipulation capabilities. High torque waist joints enable deep squatting and stooping, supporting operations requiring strength and flexibility like retrieving items from floor level storage or inspecting low equipment.
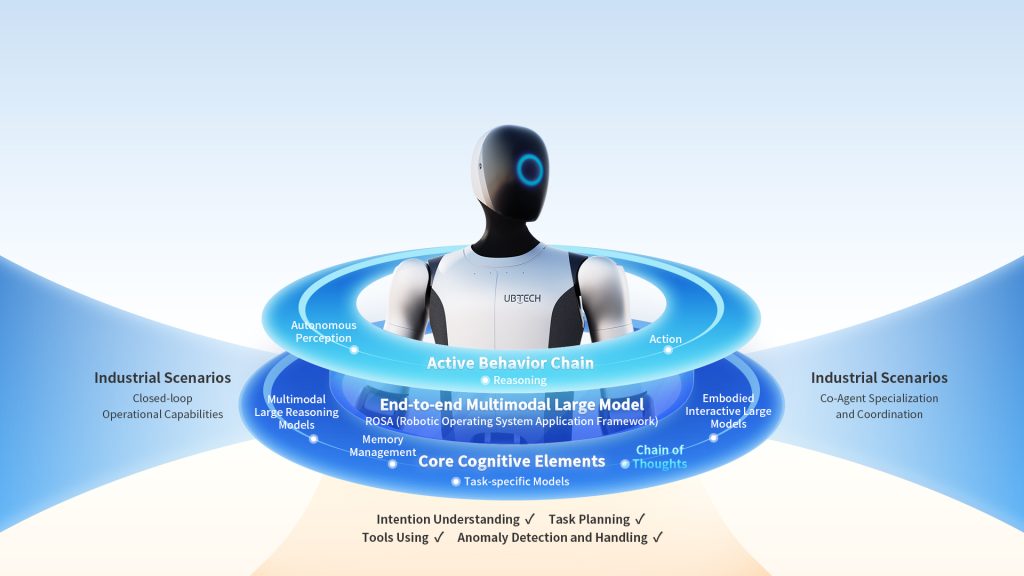
For navigation and environmental awareness, the Walker S2 integrates UBTech’s BrainNet 2.0 and Co-Agent AI frameworks combining multimodal reasoning, task planning, tool usage, and autonomous anomaly detection and handling. A pure RGB binocular stereo vision system provides human like depth perception, enabling adaptation to dense, dynamic factory environments.
Advanced dynamic balancing algorithms maintain stability during bipedal locomotion even when carrying heavy loads or moving at speeds up to 7.2 kilometers per hour (2 meters per second or 4.5 miles per hour). This walking speed places the Walker S2 among the faster humanoid robots currently available, though still well below average human jogging pace of 8-10 km/h.
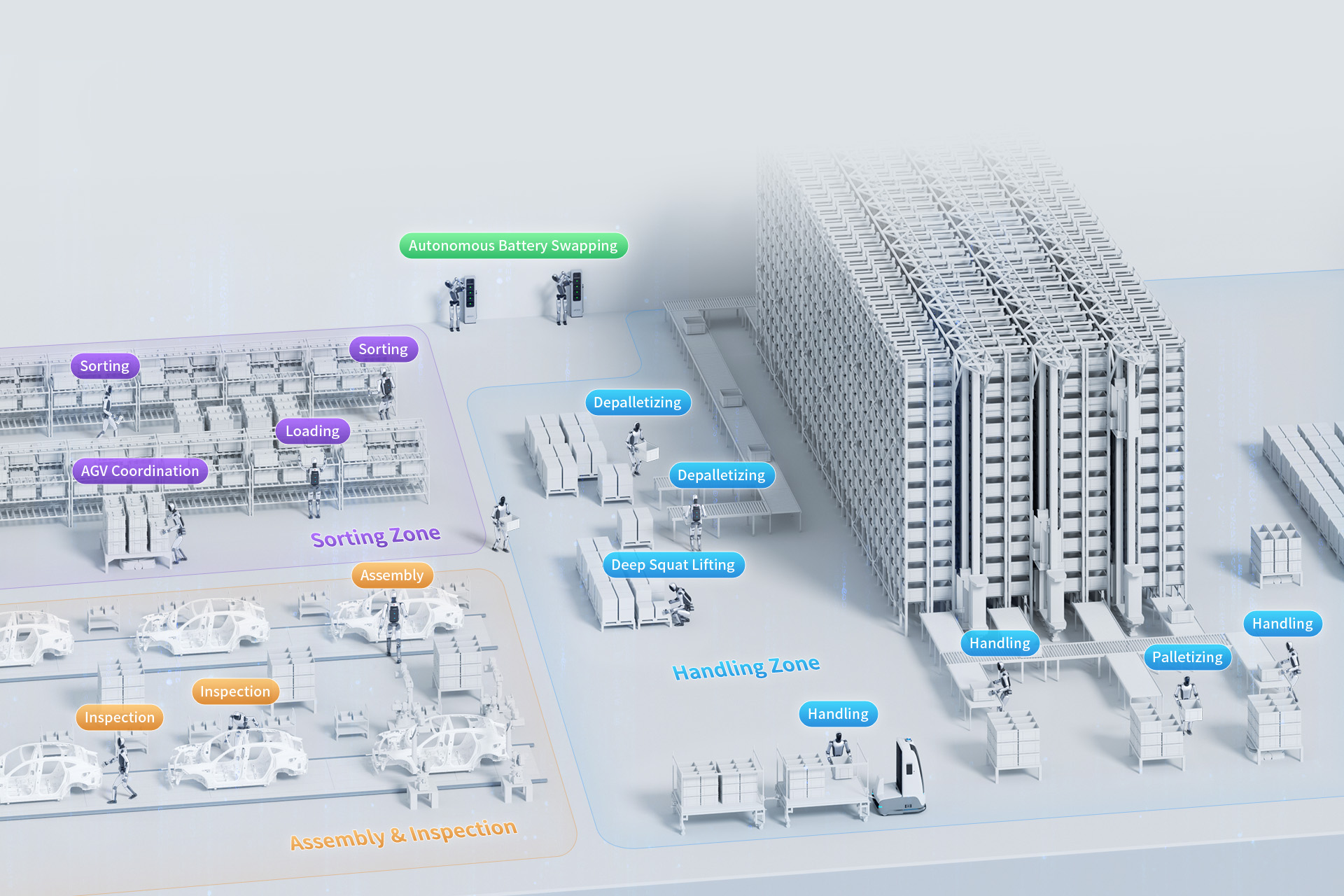
From Product to Solution: The Turnkey Approach
UBTech has shifted its delivery model from selling products to providing complete operational capabilities. The company offers what it describes as first of its kind standardized and replicable turnkey solutions. Rather than simply delivering robots and expecting customers to figure out integration, UBTech provides comprehensive deployment packages including scenario specific configuration, worker training programs, ongoing technical support, and performance optimization services.
This solution oriented approach addresses a critical adoption barrier. Many potential customers recognize humanoid robots’ potential value but lack robotics expertise to integrate them effectively into existing operations. UBTech’s turnkey model reduces this friction, enabling companies to deploy humanoids without building in house robotics teams.
The Walker S2 integrates UBTech’s Co-Agent intelligent agent system providing closed loop operational capabilities. The system empowers robots with intention understanding (interpreting complex instructions), task planning (breaking objectives into executable steps), tool usage (operating equipment and systems), and autonomous anomaly detection and handling (identifying and resolving unexpected situations). Complemented by comprehensive user training systems, this approach offers practical pathways to large scale humanoid adoption.
Production Scaling: The Path to 10,000 Annual Units
Aggressive Manufacturing Expansion Plans
UBTech has outlined an extraordinarily aggressive production ramp up targeting 500 units delivered by end of 2025, 5,000 units produced in 2026 (10x increase), and 10,000 units annually by 2027 (20x current capacity). This trajectory positions UBTech to match and potentially exceed Tesla’s projected Optimus production volumes while maintaining significant technological and commercial lead.
Chief Branding Officer Michael Tam stated the domestic supply chain has matured to the point where high precision parts, including motor systems, ball screws, and spiral bevel gears, now match global peers in quality while offering cost advantages. UBTech reports 90% of its supply chain is now localized within China, reducing dependency on international components vulnerable to geopolitical disruption.
The company operates two dedicated humanoid factories: one in Shenzhen and another in Liuzhou, Guangxi province. Tam described UBTech as one of the few firms with “full stack capabilities” combining R&D, manufacturing, and sales under one roof. This vertical integration enables rapid iteration and cost optimization impossible for companies relying on external suppliers.
The China Advantage: Scale Economics in Robotics
UBTech’s cost reduction strategy explicitly leverages the same scale economics that enabled China to dominate global electric vehicle markets. Tam stated that rapid shift of China’s supply chain toward humanoid robotics and close collaboration with upstream suppliers enables manufacturing cost declines of 20-30% annually.
This aggressive cost curve has allowed UBTech to set long term pricing targets rivaling Tesla’s Optimus ambitions. Tam predicts that by 2027 2030, unit production costs for humanoid robots could fall below $20,000. Current humanoid pricing ranges from $5,900 for basic models to $90,000+ for advanced platforms, with most industrial humanoids priced $30,000-$50,000. Reaching sub $20,000 pricing while maintaining Walker S2 capabilities would transform market accessibility.
The cost reduction pathway combines increased production volumes enabling economies of scale, component cost reductions as suppliers scale and competition intensifies, design optimization eliminating unnecessary complexity, and manufacturing process improvements reducing labor and overhead. Chinese suppliers’ willingness to invest in humanoid specific production capacity ahead of proven demand reflects government backing and confidence in market trajectory.
Financial Performance and Market Response
Revenue Growth and Path to Profitability
In the first half of 2025, UBTech reported revenue of 621 million yuan (approximately $88 million), representing 27.5% year over year growth. Gross profit reached 217 million yuan ($31 million), up 17.3%. While the company remains unprofitable with losses of 440 million yuan ($62 million) for the half year period, losses narrowed by 18.5% year over year, demonstrating improving economics as revenue scales.
Significantly, humanoids’ share of UBTech’s total sales increased from approximately 10% in 2024 to 30% in 2025, reflecting the Walker series’ commercial traction. This product mix shift toward higher value industrial humanoids should improve gross margins over time as humanoids command premium pricing compared to educational robots and consumer products that previously dominated UBTech’s revenue.
The company’s order backlog of 1.3 billion yuan significantly exceeds its current annual revenue run rate, suggesting strong revenue growth continuing through 2026 as orders convert to deliveries and revenue recognition. With 566 million yuan worth of November orders scheduled for year end delivery, Q4 2025 should show substantial revenue acceleration.
Stock Performance and Investor Sentiment
Market response to UBTech’s commercial progress has been emphatically positive. The company’s stock price gained more than 150% in 2025, closing at HK$133 (approximately $17) in late November. Brokerages including Citi and JPMorgan maintain “buy” ratings with price targets above HK$170, implying additional 28% upside from current levels.
UBTech recently secured inclusion in the MSCI China Index, a key benchmark for global investors tracking China’s innovative economy. This inclusion should attract institutional capital from index funds required to match benchmark allocations, providing additional financial resources for the company’s ambitious expansion plans.
In November 2025, UBTech announced completion of a placement financing worth HK$3.109 billion (approximately $400 million). The company disclosed that approximately 75% of funds raised, roughly $300 million, will specifically support mergers, acquisitions, and integration along the industrial chain. The focus targets upstream and downstream enterprises with potential in the humanoid robot value chain, including direct investments, target company acquisitions, or joint venture establishments.
This M&A strategy suggests UBTech intends to accelerate vertical integration and control more of its supply chain, following the playbook of successful Chinese EV manufacturers like BYD that brought component production in house to reduce costs and accelerate innovation.
Industry Context: China’s Humanoid Leadership Push
Government Support and Strategic Priorities
UBTech’s achievements reflect broader Chinese government determination to dominate global humanoid robotics. Beijing has positioned humanoids as strategic technology priority, with national policy goals targeting production at scale by 2025 and global market leadership by 2027. This backing includes massive subsidies, preferential procurement policies, streamlined regulatory approvals, and inclusion in high level economic planning initiatives.
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology recently formalized China’s national humanoid robotics committee, with UBTech executive Jiao Jichao appointed alongside founders from Unitree Robotics (Wang Xingxing) and AgiBot (Peng Zhihui) to draft the industry’s technical “rulebook.” This committee establishes unified standards for safety, hardware interfaces, and data formats, regulatory baselines critical as robots transition from controlled factories into public spaces and government operations.
Industry forecasts predict China could have 302.3 million humanoid robots in use by 2050, well ahead of U.S. projections of 77.7 million. Chinese companies are expected to dominate global production due to vertical integration advantages, government support, massive domestic markets, and willingness to deploy robots at scale before perfecting every capability.
Competitive Landscape and Market Positioning
The Chinese humanoid market features intense competition among well funded startups and established technology companies. Unitree Robotics in Hangzhou has achieved global attention with aggressive pricing strategies, offering humanoids starting at $5,900 and targeting a $7 billion IPO. AgiBot recently set a world record with its A2 humanoid walking 106 kilometers over three days, demonstrating endurance and reliability.
However, UBTech’s commercial performance clearly leads the pack. The 1.3 billion yuan order book dwarfs competitors’ announced contracts. While Unitree reported 1.1 billion yuan in cumulative orders since launching Walker series shipments, UBTech’s figure represents confirmed 2025 orders alone, excluding the company’s broader educational robotics and consumer product lines.
UBTech became the first robotics company to list on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in December 2023, providing liquidity for early investors and access to public markets for growth capital. This first mover advantage in public markets gives UBTech visibility and credibility that privately held competitors lack when competing for large enterprise and government contracts.
The company’s partnerships with China’s largest automakers, BYD, Geely, Dongfeng, FAW-Volkswagen, provide scale and operational experience competitors cannot match. These relationships generate recurring revenue as successful deployments expand to additional facilities while creating competitive moats through customization, integration depth, and institutional knowledge.
Applications Expanding Beyond Manufacturing
Government and Public Service Deployments
The 264 million yuan border deployment contract represents UBTech’s expansion into government operations with profound implications. Governments worldwide observe China’s humanoid deployments as demonstrations of technological capability and practical viability. Success at border crossings, high security environments where failures carry serious consequences, validates humanoids for numerous government applications including airport operations, courthouse security, DMV services, and emergency response.
Beyond border crossings, Chinese government entities have deployed humanoid robots at immigration checkpoints during international summits, police patrol duties in major cities including Shenzhen and Shanghai, airport customer service at facilities like Hangzhou Xiaoshan International Airport, and public facility guidance in government buildings.
These government deployments serve dual purposes: improving operational efficiency while demonstrating China’s technological leadership on the world stage. When international visitors to China encounter humanoid robots at airports and border crossings, it sends powerful messages about the nation’s technological advancement and willingness to deploy cutting edge AI systems in practical applications.
Data Collection and AI Training Infrastructure
Several of UBTech’s largest contracts involve data collection centers where humanoid robots generate training data for AI systems. The 159 million yuan Zigong facility and 126 million yuan Guangxi project both focus on embodied intelligence data collection and testing.
This infrastructure investment reflects understanding that achieving truly capable humanoid AI requires massive real world training data. Simulation provides some training data, but the complexity of real world physics, lighting, materials, and interactions cannot be fully simulated. Data collection centers allow systematic gathering of diverse scenarios under controlled conditions, accelerating AI training while generating revenue.
Chief Branding Officer Tam explicitly noted this positive feedback loop: increased deployments generate real world data that enriches simulation training data, which accelerates embodied AI development, which enables expanded deployments generating even more data. This virtuous cycle gives early leaders like UBTech compounding advantages over competitors still developing basic capabilities.
Future Outlook: What Comes Next
Short Term Execution: Delivering on Commitments
UBTech’s most immediate challenge involves executing on its commitments to deliver 500 Walker S2 units by year end 2025. With 566 million yuan worth of November orders requiring year end delivery, the company faces intense production pressure during Q4. Success demonstrates manufacturing maturity and supply chain reliability; failure raises questions about whether UBTech over committed to secure contracts.
The border deployment beginning in December represents another critical near term milestone. Unlike controlled factory environments, border operations face public scrutiny, security sensitivity, and diverse stakeholder expectations. Technical failures, security lapses, or negative public reactions could derail government adoption strategies and impact UBTech’s reputation.
Medium Term Scaling: The 2026 Production Ramp
Achieving 5,000 unit production in 2026, a 10x increase from 2025, represents extraordinary manufacturing challenge. Even with localized supply chains and dedicated factories, scaling humanoid production involves hundreds of precision components, sophisticated assembly processes, extensive testing protocols, and quality control systems.
Component suppliers must simultaneously scale to support UBTech’s expansion. Motor manufacturers, sensor suppliers, computing hardware providers, and structural component fabricators all require capacity expansions coordinated with UBTech’s timeline. Any supply chain constraints could bottleneck production and delay deliveries.
The company’s announced M&A strategy using $300 million from recent placement financing suggests plans to acquire critical suppliers or integrate vertically to control more supply chain. These acquisitions, if successful, could accelerate scaling while reducing per unit costs through vertical integration.
Long Term Vision: The Humanoid Economy
UBTech’s ambitions extend far beyond industrial applications. The company envisions humanoid robots as the ultimate form of embodied intelligence transitioning from task specific tools to autonomous entities with general intelligence capable of learning new skills through observation, adapting to novel situations without explicit programming, and handling real world complexity and variability.
Achieving this vision requires continued AI advancement, particularly in areas like common sense reasoning, long term planning, and intuitive physical interaction. Current humanoid robots remain significantly limited compared to human capabilities in strength, speed, endurance, and cognitive flexibility. However, the pace of progress suggests gaps will narrow substantially over coming decades.
The broader implications extend to labor markets, economic productivity, and social structures. If humanoid robots achieve production costs below $20,000 while performing wide ranges of physical and cognitive tasks, they could reshape industries from construction and agriculture to healthcare and hospitality. UBTech’s early lead in commercialization positions the company to capture disproportionate value as this transformation unfolds.
Conclusion: Commercial Validation at Scale
UBTech’s achievement of 1.3 billion yuan in humanoid robot orders represents far more than a financial milestone. It validates that humanoid robotics has progressed from research curiosity to commercially viable technology generating significant revenue at scale. The diversity of applications, automotive manufacturing, border security, data collection infrastructure, logistics operations, demonstrates humanoids’ versatility across multiple high value sectors.
The Walker S2’s autonomous battery swapping capability solves one of the field’s most fundamental barriers, enabling 24/7 operation that justifies the capital investment required for humanoid deployment. UBTech’s shift from product sales to turnkey solutions addresses adoption barriers for customers lacking robotics expertise. The company’s aggressive production scaling targets and cost reduction roadmap suggest confidence that current traction represents the beginning rather than peak of commercial adoption.
As the humanoid robot market surges toward projected growth of $38 billion by 2035 and potentially $5 trillion by 2050, early leaders like UBTech that establish manufacturing scale, secure major customer relationships, and accumulate operational data will capture disproportionate market share. The company’s first mover advantages in public markets, government deployments, and automotive partnerships create competitive moats difficult for rivals to overcome.
Challenges remain substantial. Production scaling, supply chain management, AI capability improvements, and competitive pressure from well funded rivals all require successful execution. However, UBTech’s track record of converting contracts to deployed robots, partnerships with China’s largest industrial companies, and government backing position the company to maintain leadership as humanoid robotics transitions from emerging technology to mainstream industrial tool.
The 1.3 billion yuan order book isn’t just a number, it’s validation that the robot revolution has moved from laboratories to factory floors, from prototypes to production, from speculation to reality. UBTech isn’t predicting the future; it’s building it, one Walker S2 at a time.